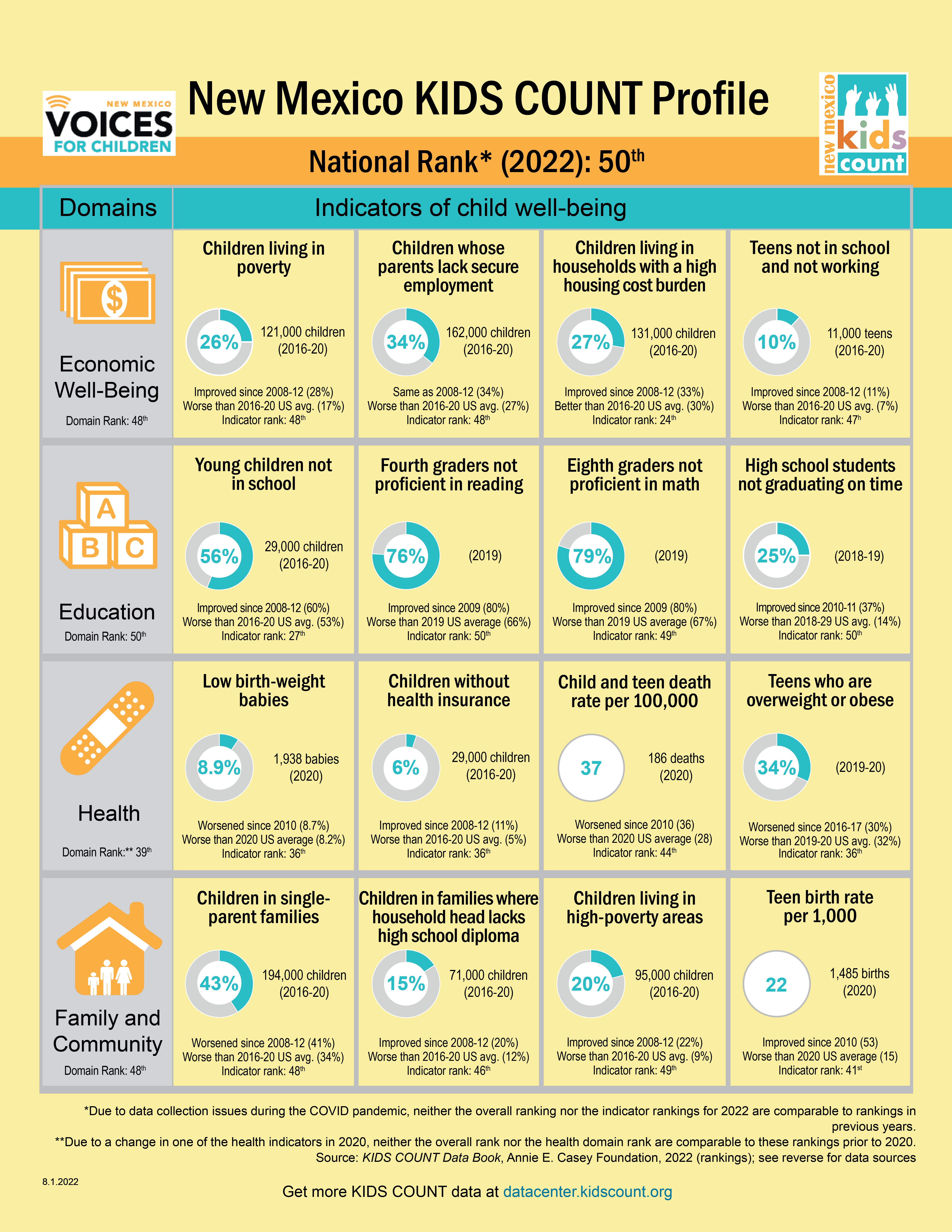
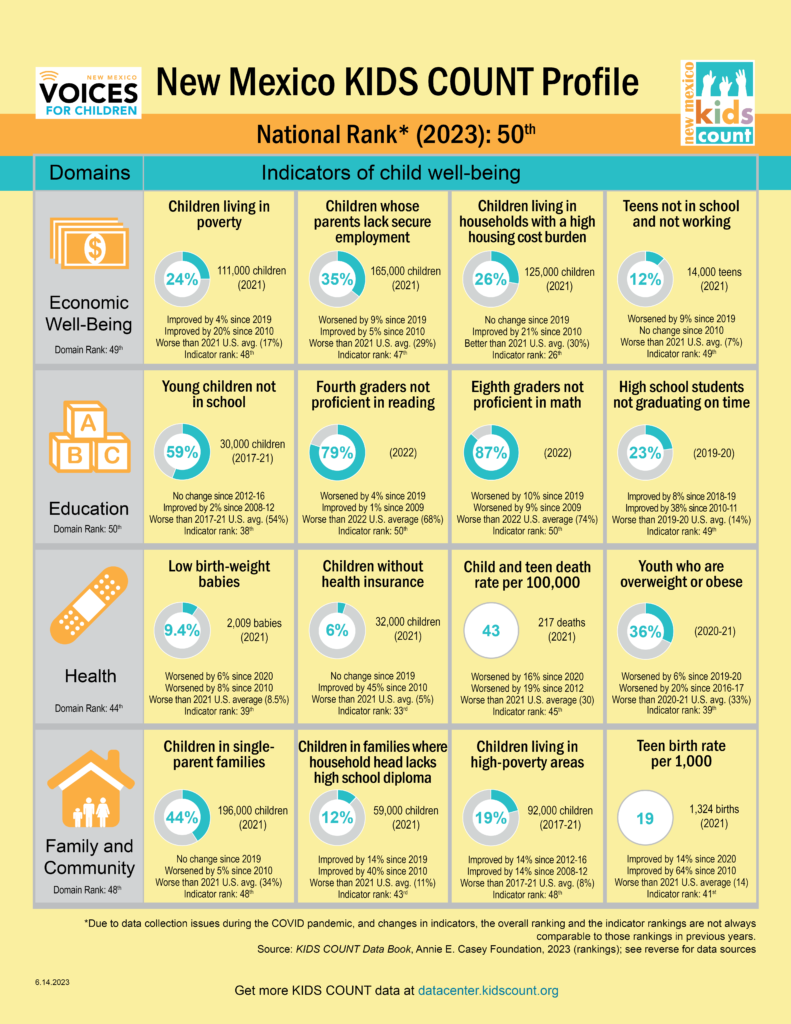
The following article appeared in the Las Cruces Sun News and other media outlets on June 30, 2023.

Once again New Mexico is at the very bottom of a list. Kids Count 2023 is compiled by the Annie E. Casey Foundation with distribution and media handled by New Mexico Voices for Children.
While it is not the report Rio Grande Foundation would compile, the 16 variables considered in do highlight issues regarding the well-being of New Mexico children. Sadly, like so many similar reports, the results are not good for our state. What is unique is the positive spin being applied by Voices for Children.
As Voices for Children’s Amber Wallin recently wrote in an opinion piece, “you shouldn’t let the rankings get you down because they don’t tell us how far we’ve come.” We politely disagree and believe that Voices would not have the same sanguine viewpoint if a Republican governor or Legislature were calling the shots.
In 2019 the organization’s then Director James Jimenez said of New Mexico’s 50th ranking, “It is very much a reflection of what happened, and more specifically, what didn’t happen during the Martinez years.”
We took a careful look through this year’s report and found that of the 16 variables, 9 of them got worse while 6 improved (one stayed the same). That is hardly cause for celebration.
Perhaps even more interesting than the overall results is New Mexico’s poor performance in four “COVID-related” indicators. In our view these include:
- 79 percent of New Mexico fourth graders are not proficient in reading. This number has dropped 4 percent since 2019;
- 87 percent of eight graders are not proficient in math. This number has dropped by 10% since 2019;
- New Mexico’s child and teen death rate per 100K worsened by 16 percent since 2020;
- The percent of youth who are overweight or obese has worsened by 6 percent since 2019-2020.
These four variables (of the 16 in the report) have significant connections to Gov. Lujan Grisham’s COVID lockdown policies that locked our kids out of school for over a year and encouraged New Mexicans to stay inside and isolate themselves from other people.
The good news is that the COVID pandemic is over, as are the Gov.’s restrictions. Sadly, as critics pointed out at the time, the impacts of her policies were clearly going to do more harm than good. Will the kids, especially those from poor families be able to recover? It is hard to say.
What is clear is that after more than four years in office and with the benefit of an unprecedented oil boom, massive spending increases haven’t improved New Mexico’s 50th-place performance. We recommend going a different direction from the government-driven status quo (a status quo that has dominated New Mexico for nearly a century).
Instead of more government programs we can use the oil and gas surplus to reform our anti-business gross receipts tax and then focus on eliminating the anti-work personal income and corporate taxes. Make New Mexico the jobs and economic growth hub of the Americans Southwest and watch as good paying jobs and economic opportunity improve education, social, and economic outcomes for our children and all New Mexicans.
We are a long way psychologically and politically from breaking out of the big-government paradigm, but it is long overdue. After all, it’s for the children.
Paul Gessing is president of New Mexico’s Rio Grande Foundation. The Rio Grande Foundation is an independent, nonpartisan, tax-exempt research and educational organization dedicated to promoting prosperity for New Mexico based on principles of limited government, economic freedom and individual responsibility


 With a drop of 4.1 percent, New Mexico’s decline is worse than EVERY state in the union with the exception of West Virginia which saw a 5.4 percent drop. Amazingly West Virginia STILL slightly outperforms New Mexico when it comes to prime working-age employment rate.
With a drop of 4.1 percent, New Mexico’s decline is worse than EVERY state in the union with the exception of West Virginia which saw a 5.4 percent drop. Amazingly West Virginia STILL slightly outperforms New Mexico when it comes to prime working-age employment rate.